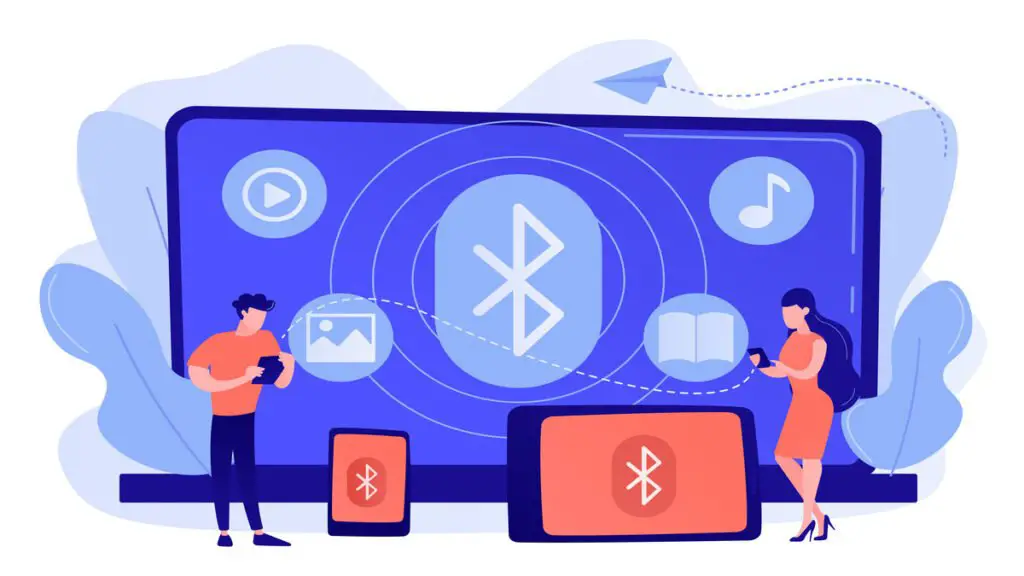
In our increasingly interconnected world, wireless communication has become an indispensable part of our lives. From smartphones and wearables to home automation and healthcare devices, the need for efficient and power-friendly wireless connectivity is ever-growing. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has emerged as a game-changing technology useful in a wide range of applications with its low power consumption. In this blog post, we will dive into the world of Bluetooth Low Energy to explore its fundamentals, advantages, applications and its potential to revolutionize the way we connect with devices.
Understanding Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless communication technology designed for low power consumption and short-range communication. It is an extension of the classic Bluetooth technology, specifically optimized for applications that prioritize energy efficiency over high data transfer rates. BLE operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band and offers seamless compatibility with existing Bluetooth devices.
Key Advantages of Bluetooth Low Energy
BLE offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications:
a. Ultra-low power consumption: BLE is designed to minimize power consumption, enabling devices to operate on small coin cell batteries for extended periods. This low power requirement makes it ideal for battery-powered devices, wearable devices and IoT applications.
b. Simplified development: BLE has a simplified protocol stack and a smaller footprint compared to classic Bluetooth, making it easier to implement and integrate into devices. This simplicity translates into reduced development time and cost.
c. Fast connection establishment: BLE devices can establish connections quickly, enabling efficient data transfer while conserving power. This feature is particularly advantageous for applications that require intermittent or periodic communication.
d. Enhanced security: BLE incorporates robust security features to protect data during transmission. Encryption and authentication mechanisms provide a secure communication channel, safeguarding sensitive information.
e. Interoperability: BLE maintains backward compatibility with classic Bluetooth, allowing seamless communication between BLE-enabled devices and existing Bluetooth devices. This interoperability expands the potential connectivity options and simplifies integration into existing ecosystems.
BLE Applications: Transforming Industries
Bluetooth Low Energy has a vast range of applications across various industries, including:
a. Wearables and Fitness: BLE is extensively used in fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitoring devices. Its low power consumption, compact size, and ability to connect with smartphones and other peripherals make it an ideal technology for wearable applications.
b. Home Automation: BLE enables smart home devices to communicate with each other, offering seamless control and automation capabilities. From smart lighting and thermostats to security systems and voice assistants, BLE simplifies the integration and control of interconnected devices within the home ecosystem.
c. Asset Tracking: BLE beacons and tags provide efficient and cost-effective asset tracking solutions. Whether it’s tracking inventory in retail stores, monitoring equipment in industrial settings, or locating lost items, BLE-based tracking systems offer real-time tracking and geolocation capabilities.
d. Healthcare and Medical Devices: BLE plays a significant role in remote patient monitoring, health tracking, and medical device connectivity. From wireless sensors for vital signs monitoring to medication adherence devices, BLE facilitates seamless communication between devices and healthcare systems, enhancing patient care and enabling telehealth applications.
e. Proximity-based Services: BLE beacons enable proximity-based services, offering personalized experiences and location-based information in public spaces like shopping malls, museums, and airports. From personalized offers and navigation assistance to interactive exhibits, BLE-powered beacons enhance the user experience in various contexts.
BLE Development: Tools and Frameworks
Developing BLE applications requires knowledge of the BLE protocol stack and the use of appropriate tools and frameworks. Some commonly used resources include:
a. BLE Development Kits: Various manufacturers provide development kits that include BLE modules, software development tools, and documentation. These kits help developers prototype and test their BLE applications efficiently.
b. BLE Software Development Kits (SDKs): SDKs provide a set of libraries, APIs, and tools specific to BLE development. They simplify the implementation of BLE functionality, such as establishing connections, data exchange, and handling BLE profiles.
c. BLE Testing and Debugging Tools: Testing and debugging are crucial aspects of BLE development. Tools like Bluetooth sniffers, protocol analyzers, and debugging hardware assist in identifying and resolving issues related to connectivity, data transmission, and power consumption.
d. Cross-Platform Development Frameworks: Cross-platform frameworks like Xamarin, React Native, and Flutter provide abstractions for developing BLE applications that can run on multiple platforms, such as iOS and Android. These frameworks streamline the development process and reduce time to market.
Future Trends and Possibilities
The future of Bluetooth Low Energy holds exciting possibilities. Some emerging trends include:
a. BLE Mesh Networking: BLE Mesh extends the capabilities of BLE by enabling devices to form large-scale networks. This advancement opens up opportunities for applications like smart lighting, asset tracking, and industrial automation, where devices need to communicate and interact within a mesh network.
b. BLE 5.x and Beyond: The Bluetooth SIG continues to enhance the BLE standard with each iteration. BLE 5.x introduced features like increased range, higher data transfer rates, and improved coexistence with other wireless technologies. Future versions of BLE are expected to push the boundaries further, enabling even more advanced applications.
c. BLE in Industrial IoT: The combination of BLE’s low power consumption, robustness, and interoperability makes it suitable for industrial IoT applications. From asset tracking in warehouses to sensor networks in manufacturing plants, BLE is poised to play a significant role in Industry 4.0 and industrial automation.
d. BLE in Healthcare Innovations: Bluetooth Low Energy has immense potential in healthcare, contributing to advancements in remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and personalized medicine. With the proliferation of wearable devices and the need for seamless connectivity between healthcare systems, BLE will continue to drive healthcare innovations.
Conclusion
Bluetooth Low Energy has revolutionized wireless connectivity by providing a power-efficient and versatile solution for a wide range of applications. Its low power consumption, simplified development process, and interoperability have made it a preferred choice in industries such as wearables, home automation, asset tracking, healthcare, and proximity-based services. As BLE continues to evolve and new advancements emerge, the possibilities for innovation and connectivity are limitless. By embracing BLE’s capabilities, developers and manufacturers can create smarter, more efficient, and interconnected devices that shape the future of our connected world.