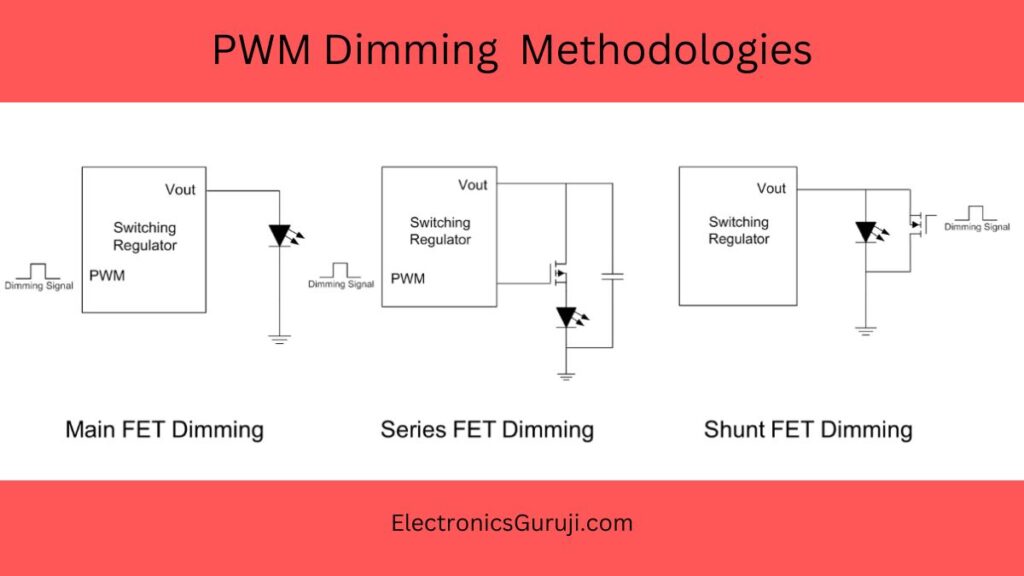
As LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting technology continues to evolve, various dimming methods have emerged to offer users control over brightness levels. Among these methods, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) dimming has gained prominence for its efficiency and precise control in regulating LED light output. PWM dimming is a prevalent method used to regulate the brightness of LED lights by manipulating the duty cycle of electrical pulses.
Evolution of LED Dimming Technology:
LEDs, known for their energy efficiency and durability, have replaced conventional lighting sources in many applications. The need for dimmable LED lights led to the development of different dimming methods, each with its unique approach to adjusting brightness levels.
How PWM Dimming Works
In PWM dimming, the LED brightness is controlled by rapidly switching the LED current on and off at a fixed frequency. The ratio of the time the LED is on (duty cycle) to the time it’s off determines the perceived brightness. For instance, a higher duty cycle (more on-time) results in greater brightness, while a lower duty cycle (more off-time) reduces brightness.
Significance of Frequency and Duty Cycle
- Frequency: The frequency of the electrical pulses defines how quickly the LED turns on and off. A higher frequency generally reduces flickering and enhances dimming performance.
- Duty Cycle: The duty cycle denotes the proportion of time the LED remains on within each cycle. Adjusting this cycle alters the brightness levels.
Advantages of PWM Dimming in LED Lights
Precise Control and Flicker-Free Dimming
PWM dimming offers precise control over LED brightness, allowing for fine adjustments. Additionally, when implemented effectively, PWM dimming can produce flicker-free lighting, contributing to a comfortable user experience.
Efficiency in Dimming
The on-off switching characteristic of PWM dimming can result in higher efficiency compared to analog methods like 0-10V dimming. It allows LEDs to operate at their optimal efficiency levels even at lower brightness settings.
Considerations and Limitations
Audible Noise and EMI Concerns
Some PWM dimming systems might produce audible noise, especially at lower dimming levels. Moreover, electromagnetic interference (EMI) can occur due to rapid switching, requiring proper shielding and design considerations.
Compatibility and Quality of Dimming
Compatibility with LED drivers and fixtures is crucial for optimal PWM dimming performance. Additionally, the perceived quality of dimming might vary among different LED models and dimming systems.
Applications and Future Trends
Versatile Applications
PWM dimming finds applications in various settings, including residential, commercial, and automotive lighting. Its flexibility and efficiency make it suitable for diverse lighting environments.
Advancements in Dimming Technology
The future of PWM dimming involves advancements in driver design, integration with smart systems, and optimization for enhanced efficiency and dimming quality.
Conclusion
PWM dimming stands as a versatile method for controlling LED brightness, offering precise adjustments and efficiency benefits. Despite some considerations regarding noise and compatibility, PWM dimming continues to be a prominent technology in the realm of LED lighting.
FAQs
How does PWM dimming differ from other dimming methods like 0-10V dimming?
PWM dimming regulates LED brightness by rapidly switching the LED current on and off at a fixed frequency, altering the duty cycle to control brightness levels. In contrast, 0-10V dimming modulates the voltage supplied to LEDs, offering continuous and smooth control over brightness without rapid on-off cycles.
What are the advantages of PWM dimming in terms of efficiency?
PWM dimming can enhance efficiency by allowing LEDs to operate at optimal efficiency levels even at lower brightness settings. Its on-off switching characteristic contributes to maintaining efficiency while providing varying brightness levels.
Are there any concerns regarding flickering in PWM dimming?
When implemented effectively, PWM dimming can produce flicker-free lighting. However, at low frequencies or improper implementation, flickering might occur, potentially impacting user comfort. Proper frequency settings and quality components help mitigate this concern.
In what applications is PWM dimming commonly used for LED lights?
PWM dimming finds versatile applications across residential, commercial, and automotive lighting. Its precise control and efficiency make it suitable for diverse environments where varying brightness levels are desired.
What are the anticipated future developments in PWM dimming technology for LED lighting?
Future advancements in PWM dimming technology focus on optimizing driver design, integrating with smart systems for enhanced control, and improving efficiency and dimming quality. These developments aim to further refine the user experience and expand the applications of PWM dimming.